Almost half of all adults have some form of gum disease. The main culprit is the accumulation of plaque and tartar on teeth. The longer they are present, the more harmful they become. The plaque’s bacteria cause inflammation of the gums. In its milder form (gingivitis) the gums become red, swollen and can bleed easily. In its more advanced forms (periodontitis), the inflammation process leads to gum recession, bone loss, and even tooth loss as the connecting tissue that support the teeth are destroyed.
Managing gum disease with frequent regular cleanings and checkups is important for both oral health and systemic health. If left untreated, it can introduce the inflammation throughout the body and contribute to other issues with heart, brain, lungs, liver, kidneys, artificial joints, and prenatal development.
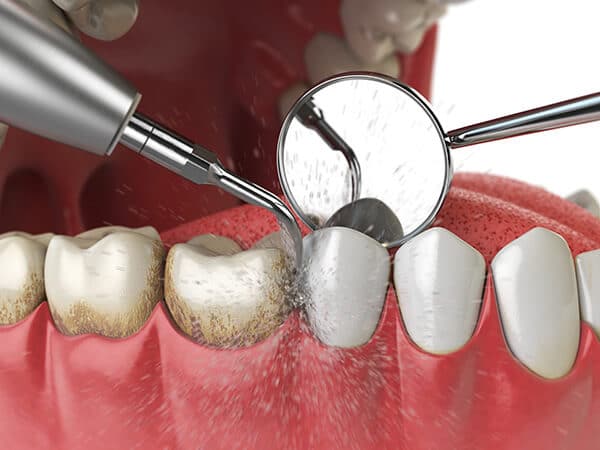
Our commitment to keeping your mouth healthy includes treating the underlying problem of periodontal disease. By reinforcing good hygiene habits, we’ll help you prevent further damage to your gums. With frequent cleanings and gum treatments we’ll reduce the bacterial load that has been causing chronic inflammation. Scaling and Root Planing is a careful cleaning of the root surfaces to remove plaque and calculus from deep periodontal pockets in the gums. Removing the plaque and tartar give the gums their best chance to heal and prevent further damage to the tissues that support your teeth. Take the time to address your gum health and improve the quality of your overall health. We will be happy to discuss any additional medicaments, rinses, or other treatments that may benefit you.,
